- Best PCD Pharma Franchise Company
- +91 9216295095
- hcareindia@gmail.com
Understanding Bronchial Asthma and Managing its Symptoms

Pharma Franchise for General Range
How to Spot, Diagnose COPD Symptoms and Prevent Long-Term Damage
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Bronchial Asthma?
Bronchial asthma is a chronic respiratory disease characterized by reversible chronic inflammation of the airways, which causes recurrent episodes of wheezing, breathlessness, chest tightness and coughing. These symptoms can be mild or severe that vary over time and in intensity with airflow limitation. It can make even the simplest tasks like walking or climbing stairs a daunting experience.
12% of Adults and 15% of Children are affected by the disease.
In Kids: Males are more prone to asthma than females
In Adult: Male = Female
In Elderly: Females are more prone to this disease than males
Do you go through recurrent episodes of wheezing, breathlessness, chest tightness and coughing? Breathing can be a daily struggle for people living with bronchial asthma.
Here we will delve into the causes, symptoms, types, diagnosis and treatments of bronchial asthma, as well as tips on managing the condition to breathe easy.
Classification of Asthma
Asthma is usually associated with airway hyperresponsiveness and airway inflammation, but these are not sufficient to make the diagnosis. Diagnosis of asthma is based on the history of characteristic symptom patterns and evidence of expiratory airflow limitation.
What are the Symptoms of Bronchial Asthma?
Bronchial asthma symptoms vary from person to person and range from mild to severe. The most common symptoms of bronchial asthma include:
- Wheezing: a whistling sound when breathing.
- Breathlessness: difficulty breathing, shortness of breath or rapid breathing.
- Chest tightness: a feeling of pressure or tightness in the chest.
- Coughing: a persistent cough, especially at night or early in the morning.
These symptoms can occur at any time, but they are most likely to occur at night or early in the morning. In severe cases, asthma symptoms can be life-threatening, and immediate medical attention is required.
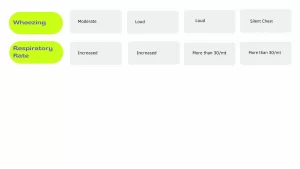
What are the Symptoms of Acute Severe Asthma?
Symptoms of acute severe asthma are:
- If person speaks in words due to breathlessness
- Use of accessory muscles for respiration
- Patient is usually agitated
- Heart Rate > 120/min
- Oxygen saturation < 90%
- PEFR: 25-40 ml/min
Medical management / ICU admission may be required.
Types of Bronchial Asthma
There are several types of bronchial asthma, including:
- Allergic asthma: is triggered by allergens such as pollen and dust mites.
- Non-allergic asthma: is triggered by irritants such as smoke, pollution and strong odours.
- Exercise-induced asthma: is triggered by physical activity.
- Occupational asthma: is triggered by exposure to workplace irritants such as chemicals, dust and fumes.
- Childhood asthma: is the asthma associated with allergic rhinitis (80%) that develops in childhood and may improve or disappear as the child grows older.
Each type of asthma require different treatments, and it is essential to work with your doctor to develop a treatment plan that works for you.
Causes of Bronchial Asthma
Bronchial asthma is a complex disease, and its exact cause is still unknown.
Various triggering stimuli
⇓
Airway Inflammation
⇓
Airway obstruction due to airway hyperresponsiveness
⇓
Reversible Chronic Asthma
However, several factors are known to trigger asthma symptoms. These triggers can vary from person to person which includes:
- Allergens: such as pollen, dust mites, viruses, bacteria, cigarettes or other pollutants.
- Irritants: such as smoke, pollution, paint fumes and strong odours.
- Upper Respiratory Infections: such as the common cold, flu and sinus infections.
- Exercise: physical activity can trigger asthma symptoms in some people.
- Emotional stress: stress and anxiety can cause asthma symptoms in some people.
- Weather changes: cold air, humidity and changes in temperature can trigger asthma symptoms.
It is important to note that not everyone with asthma will have the same triggers. Some people may have multiple triggers, while others may have none at all. Identifying and avoiding triggers is an essential part of managing bronchial asthma.
Risk Factors
- Obesity: especially in childhood
- Diet: saturated fatty acids
- Hygiene hypothesis
Diagnosis of Bronchial Asthma
If you are experiencing symptoms of bronchial asthma, it is important to see a doctor for a proper diagnosis. Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history and may perform several tests, including:
- Spirometry: a lung function test that measures how much air you can exhale after forceful maximal inspiration and how quickly.
- Peak flow measurement: a test that measures how fast you can exhale.
- Allergy testing: a test to determine if you have any allergies that may be triggering your asthma symptoms.
- Chest X-ray or CT scan: to rule out other conditions that may be causing your symptoms.
Once a diagnosis is made, your doctor will work with you to develop a treatment plan.
How to Manage Bronchial Asthma: Medications and Lifestyle Changes?
The goal of asthma treatment is to control symptoms and prevent asthma attacks. Treatment may include medications and lifestyle changes. Medications used to treat bronchial asthma include:
Inhaled corticosteroids
Inhaled Corticosteroids like Beclomethasone dipropionate, Budesonide can reduce inflammation in the airways and prevent asthma attacks.
Short-acting bronchodilators
Short-acting bronchodilators like Levosalbutamol, which are β-adrenergic receptor, relieve symptoms of asthma by relaxing the muscles in the airways.
Long-acting bronchodilators
Long-acting bronchodilators are used in combination with inhaled corticosteroids to control symptoms of asthma.
Leukotriene modifiers
They reduce inflammation in the airways and prevent asthma attacks.
Immunomodulators
Immunomodulators are used to treat severe asthma that is not well controlled with other medications.
Lifestyle Changes That Help Manage Bronchial Asthma
- Avoid triggers: identify and avoid triggers that cause asthma symptoms.
- Maintain a healthy weight: being overweight can make asthma symptoms worse.
- Exercise regularly: regular exercise can improve lung function and reduce asthma symptoms.
- Quit smoking: smoking can make asthma symptoms worse and increase the risk of other health problems.
It is essential to work with your doctor to develop a treatment plan that works for you.
Some Tips to Prevent Asthma Attacks
Preventing asthma attacks is an essential part of managing bronchial asthma. Here are some tips to prevent asthma attacks:
- Take medications as prescribed: taking medications as prescribed by your doctor can help prevent asthma attacks.
- Identify and avoid triggers: identifying and avoiding triggers that cause asthma symptoms is essential.
- Monitor your symptoms: monitoring your symptoms can help you identify when an asthma attack is coming.
- Have an asthma action plan: having an asthma action plan in place can help you know what to do in case of an asthma attack.
It is important to work with your doctor to develop an asthma action plan that works for you.
What are the Various Alternative Therapies for Bronchial Asthma?
Some people may choose alternative therapies. While there is limited scientific evidence to support the effectiveness of alternative therapies for asthma, some may find them helpful. Alternative therapies include:
- Acupuncture: may help reduce asthma symptoms and improve lung function.
- Breathing exercises: such as yoga and pranayama, may help improve lung function and reduce stress.
- Herbal remedies: such as ginger and turmeric, may have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce inflammation in the airways.
It is important to talk to your doctor before trying any alternative therapies for bronchial asthma.
Coping with Bronchial Asthma: Tips for Daily Life
Living with asthma can be challenging, but there are things you can do to make life easier. Here are some tips for coping with it:
- Stay informed: learn as much as you can about it and how to manage it.
- Keep a diary: keeping a diary of your symptoms and triggers can help you identify patterns and manage your asthma.
- Stay active: regular exercise can improve lung function and reduce asthma symptoms.
- Practice relaxation techniques: such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga, can help reduce stress and improve lung function.
It is important to work with your doctor to develop a plan that works for you.
Conclusion: Living with Asthma
Bronchial asthma is a chronic respiratory disease that affects millions of people worldwide. While there is no cure for bronchial asthma, it can be managed with proper understanding and treatment.
Identifying and avoiding triggers, taking prescribed medications and making lifestyle changes can help prevent asthma attacks and improve quality of life.
If you are having asthma, it is important to work with your doctor to develop a treatment plan that works for you. With proper management, people with asthma can lead healthy and fulfilling lives.